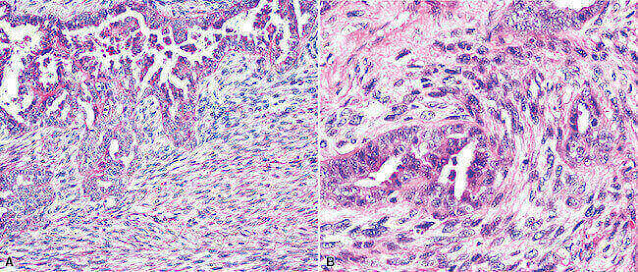
Epithelioid mesothelioma is a cancer caused by mutations in the epithelial cells associated with asbestos. About 70 percent of cases of mesothelioma involve the epithelioid cell type. This is a better prognosis than other cell types because it is less aggressive. There are three types of mesothelioma cells: epithelioid, sarcomoid and biphasic. Epithelioid mesothelioma is not only the most common. It also the best studied and has the best prognosis.
What is Epithelioid Mesothelioma?
The epithelioid cells in the body are very common and they are also healthy. They become dangerous if they mutate into fatal epithelioid mesothelioma cells after exposure to asbestos. People with epithelioid mesothelioma have a better prognosis. Other the treatment options are available compared to those with sarcomatous or biphasic cell types. The mesothelioma cancer is a mutation of a previously healthy cell. Cells are programmed to perform a specific task to divide. And when they get old, they are programmed to die. The genetic changes in normal cells allow them to ignore their programmed death and continue to divide.
Epithelioid mesothelioma cells are one of the four tissue types found in the body. They form the lining for organs, caries and our skin. When exposed to a carcinogen (eg, asbestos), it causes genetic changes that make these cells cancerous. About 50 to 70 percent of all mesothelioma cases are epitheloids. Which means that it has studied the most and has the best prognosis.
Epithelioid pleural mesothelioma refers to a specific type of mesothelioma. It concerns the protective tissue around the lungs, the pleura. And where there are the epithelioid cells that look like small, square cells with a tubular configuration and visible nucleus. When these cells are become cancerous, they are called epithelioid cells. Epithelioid mesothelioma cells themselves are not cancerous, but mutate into a form of cancer. The mesothelioma (the membrane that lines various body cavities) consists of epithelioid cells. And when such as mutations occur, a mesothelioma of the epithelioid cell type develops.
When investigating the cause of an epithelioid mesothelioma, exposure to asbestos is the only known cause. However, there are a variety of risk factors that prove to be potential factors in the development of the disease. Mesothelioma develops in mesothelioma, a layer of epithelioid cells. When epithelioid cells of mesothelioma become cancerous, they change in appearance. And pick up patterns called epithelioid, sarcomas, or biphasic. Epithelioid mesothelioma, also known as epithelioid mesothelioma, is the most common type of asbestos-related disease.
Epithelioid mesothelioma cells are one of the four tissue types found in the body. They form the lining for organs, caries and our skin. When exposed to a carcinogen (eg, asbestos), it causes genetic changes that make these cells cancerous. About 50 to 70 percent of all mesothelioma cases are epitheloids. Which means that it has studied the most and has the best prognosis.
Epithelioid pleural mesothelioma refers to a specific type of mesothelioma. It concerns the protective tissue around the lungs, the pleura. And where there are the epithelioid cells that look like small, square cells with a tubular configuration and visible nucleus. When these cells are become cancerous, they are called epithelioid cells. Epithelioid mesothelioma cells themselves are not cancerous, but mutate into a form of cancer. The mesothelioma (the membrane that lines various body cavities) consists of epithelioid cells. And when such as mutations occur, a mesothelioma of the epithelioid cell type develops.
When investigating the cause of an epithelioid mesothelioma, exposure to asbestos is the only known cause. However, there are a variety of risk factors that prove to be potential factors in the development of the disease. Mesothelioma develops in mesothelioma, a layer of epithelioid cells. When epithelioid cells of mesothelioma become cancerous, they change in appearance. And pick up patterns called epithelioid, sarcomas, or biphasic. Epithelioid mesothelioma, also known as epithelioid mesothelioma, is the most common type of asbestos-related disease.
How Is It Diagnosed?
The epithelioid mesothelioma is difficult to differentiate from certain other cancers such as adenocarcinoma. Adenocarcinoma is formed from glandular epithelioid cells. This is the most common form of lung cancer, but can occur anywhere where mucus-producing epithelioid cells are present.
For physicians, it is important to exclude adenocarcinoma before treatment. The treatment protocols are different from mesothelioma.
Recently, researchers have discovered several patches. When applied to the cells and then viewed under a microscope, you can see the patient's cancer. Research continues to reduce the likelihood of a false diagnosis. Epithelioid cells can not be identified by diagnostic imaging. To determine which cell type is present. The doctors need to perform a thoracoscopy or a similar form of surgical biopsy. Biopsies allow physicians to examine potentially cancerous cells under a strong microscope. During the biopsy, a tissue sample of the tumor is taken for further evaluation of the cells contained therein.
Diagnosis of the mesothelioma cell type of a patient is the most important stage of the diagnostic process. Knowing the cell type of the patient helps clinicians to determine the best course of the treatment.
After the surgeons biopsied the diseased tissue, they send the sample to a pathologist. General oncologists and surgeons can estimate the diagnosis based on a patient's symptoms. But only the pathologists can confirm the diagnosis and the cell type. Pathologists examine tissue samples under a microscope and look for the properties of cancer cells.
For physicians, it is important to exclude adenocarcinoma before treatment. The treatment protocols are different from mesothelioma.
Recently, researchers have discovered several patches. When applied to the cells and then viewed under a microscope, you can see the patient's cancer. Research continues to reduce the likelihood of a false diagnosis. Epithelioid cells can not be identified by diagnostic imaging. To determine which cell type is present. The doctors need to perform a thoracoscopy or a similar form of surgical biopsy. Biopsies allow physicians to examine potentially cancerous cells under a strong microscope. During the biopsy, a tissue sample of the tumor is taken for further evaluation of the cells contained therein.
Diagnosis of the mesothelioma cell type of a patient is the most important stage of the diagnostic process. Knowing the cell type of the patient helps clinicians to determine the best course of the treatment.
After the surgeons biopsied the diseased tissue, they send the sample to a pathologist. General oncologists and surgeons can estimate the diagnosis based on a patient's symptoms. But only the pathologists can confirm the diagnosis and the cell type. Pathologists examine tissue samples under a microscope and look for the properties of cancer cells.
Where It Occurs
Epithelioid mesothelioma most commonly occurs in the pleural cavity - in the lungs. In fact, the 70 percent of all cases of pleural mesothelioma are epithelioid. The other common sites for mesothelioma (stomach and very rarely the lining of the heart) are more often sarcomatous or biphasic.
Epithelioid pleural mesothelioma can be difficult to diagnose. The patients often visit their family doctor with complaints of chest pain or respiratory distress. A referral to the pulmonologist is common before an oncologist (cancer doctor) is consulted.
The rapid diagnosis of a pleural mesothelioma can be problematic because the symptoms only become visible after the cancer has progressed. These symptoms often the mimic even less severe respiratory diseases. Like asthma or pneumonia, which can lead to an initial misdiagnosis.
Once of the symptoms of a pleural mesothelioma are detected, additional diagnostic tests such as imaging scans are performed. Tumor samples are tested to confirm the presence of cancer. For the detection of epithelioid cells an experienced pathologist is required. Who analyzes to the tumor samples to determine in which cell type is present? There are the subtypes of epithelioid mesothelioma that an experienced pathologist can test for. And they know how to differentiate these cells from cells of other cancers.
Because epithelioid pleural mesothelioma can resemble adenocarcinoma cells. For an experienced pathologist, it is important to analyze the tumor samples.
Epithelioid pleural mesothelioma can be difficult to diagnose. The patients often visit their family doctor with complaints of chest pain or respiratory distress. A referral to the pulmonologist is common before an oncologist (cancer doctor) is consulted.
The rapid diagnosis of a pleural mesothelioma can be problematic because the symptoms only become visible after the cancer has progressed. These symptoms often the mimic even less severe respiratory diseases. Like asthma or pneumonia, which can lead to an initial misdiagnosis.
Once of the symptoms of a pleural mesothelioma are detected, additional diagnostic tests such as imaging scans are performed. Tumor samples are tested to confirm the presence of cancer. For the detection of epithelioid cells an experienced pathologist is required. Who analyzes to the tumor samples to determine in which cell type is present? There are the subtypes of epithelioid mesothelioma that an experienced pathologist can test for. And they know how to differentiate these cells from cells of other cancers.
Because epithelioid pleural mesothelioma can resemble adenocarcinoma cells. For an experienced pathologist, it is important to analyze the tumor samples.
How It Develops
The epithelioid mesothelioma develops when epithelioid cells mutate into cancer cells - that is. The cells that is no longer the fulfill their original purpose and are divided uncontrollably. In rare cases, asbestos exposure causes the mutation.
The type of asbestos exposure most likely to cause mesothelioma has tiny, needle-like fibers that penetrate the lungs when inhaled. Over time, they work their way through the interior of the lungs to external food. This leads to inflammation and irritation in the lining of the pleural mesothelioma cavity. Which consists of epithelioid cells. Gradually, the epithelial cells are genetically modified and carcinogenic. Occasionally, asbestos can invade other organs and cause mesotheliomas in various places. That's not common.
The different features help the pathologists distinguish the subtypes of the epithelioid mesothelioma. For example, the tubulopapillary the epithelioid mesothelioma cells form a cube-like shape. Histiocytoid cells resemble lung macrophages and poorly differentiated cells are round or irregular in shape.
The type of asbestos exposure most likely to cause mesothelioma has tiny, needle-like fibers that penetrate the lungs when inhaled. Over time, they work their way through the interior of the lungs to external food. This leads to inflammation and irritation in the lining of the pleural mesothelioma cavity. Which consists of epithelioid cells. Gradually, the epithelial cells are genetically modified and carcinogenic. Occasionally, asbestos can invade other organs and cause mesotheliomas in various places. That's not common.
The different features help the pathologists distinguish the subtypes of the epithelioid mesothelioma. For example, the tubulopapillary the epithelioid mesothelioma cells form a cube-like shape. Histiocytoid cells resemble lung macrophages and poorly differentiated cells are round or irregular in shape.
Statistics on all epithelioid subtypes are not available. It is known that a decidorium epithelioid mesothelioma accounts for about 2 to 5 percent of mesothelioma cases. And the small cells account for less than the 6 percent. Most epithelioid cases have a tubulopapillary cell pattern, and rare cases are adenoid cysts or signet rings. The diagnosis of mesothelioma can be extremely stressful. The sooner is the cancer is diagnosed, the better the treatment options and the life expectancy of the patient. A misdiagnosis and a long latency often prevent early detection, ie when symptoms of mesothelioma are detected. It is important that the person concerned consult a doctor as soon as possible and consult a mesothelioma specialist.
One of the biggest challenges in diagnosing epithelioid mesothelioma is to distinguish it from other cancers. Cancer in epithelioid tissue can be a range of malignancies, so extensive research is important. Epithelioid mesothelioma is often confused with adenocarcinoma. A common cancer that develops in the lungs, chest and colon. The glandular mesothelioma, a subtype of epithelioid cells, may resemble adenocarcinoma of the lung.
One of the biggest challenges in diagnosing epithelioid mesothelioma is to distinguish it from other cancers. Cancer in epithelioid tissue can be a range of malignancies, so extensive research is important. Epithelioid mesothelioma is often confused with adenocarcinoma. A common cancer that develops in the lungs, chest and colon. The glandular mesothelioma, a subtype of epithelioid cells, may resemble adenocarcinoma of the lung.
What Is the Best Epithelioid Mesothelioma Treatment?
Epithelioid mesothelioma responds better to treatment than sarcoma or biphasic mesothelioma. It is the less aggressive and metastasizes more slowly than other cell types. This means that surgery on epithelioid patients is more effective because their cancer cells do not spread so quickly. It depending on the stage of a patient's cancer, there are aggressive treatments that can improve a patient's prognosis.
Treatment for mesothelioma cancer usually depends on the type and stage of the cancer, not the cell type. It means that the treatment of epithelioid pleural mesothelioma is similar to the treatment of other mesothelioma cell types. Chemotherapy, radiotherapy and surgery may be possible for patients with epithelial pleural mesothelioma.
Patients with epithelial pleural mesothelioma may be required to adopt a more aggressive treatment regimen for proven epithelial cells that have been shown to be more responsive to treatment. And maybe the better prognosis than the patients with other cell types. The biopsies are the one of the first steps in establishing a general treatment plan. For example, if an early epithelioid malignant mesothelioma gets caught, surgery. And chemotherapy is probably treatment options. However, the late diagnosis may limit patients to the palliative care because they are too weak to handle treatment side effects.
Because epithelioid mesothelioma cells respond best to treatment. A patient of this nature may be considered for a more aggressive treatment plan. Patients with epithelioid mesothelioma who have been diagnosed with cancer cells are often suitable for multimodal therapy. It tries to kill cancer cells with several types or therapeutic methods. The multimodal therapy combines the most of effective cancer therapies for mesothelioma, including surgery, chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
Dr. David Sugarbaker's impressive survival in 1999 led to a group of pleural mesothelioma. Patients with malignant epithelioid cells received multimodal therapy, including extrapleural pneumonectomy, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy. About 46 percent of patients had epithelioid cell types. No of lymph node involvement and no remaining cancer cells after surgery lived for at least five years. It typical 5-year survival of mesothelioma cancer is about 10 percent.
Less than half of the epithelial patients are suitable for aggressive surgery and multimodal therapy. And more than half are diagnosed too late, regardless of cell type, to qualify for surgery. If surgery is not possible, chemotherapy is considered standard therapy and clinical trials are discussed.
Treatment for mesothelioma cancer usually depends on the type and stage of the cancer, not the cell type. It means that the treatment of epithelioid pleural mesothelioma is similar to the treatment of other mesothelioma cell types. Chemotherapy, radiotherapy and surgery may be possible for patients with epithelial pleural mesothelioma.
Patients with epithelial pleural mesothelioma may be required to adopt a more aggressive treatment regimen for proven epithelial cells that have been shown to be more responsive to treatment. And maybe the better prognosis than the patients with other cell types. The biopsies are the one of the first steps in establishing a general treatment plan. For example, if an early epithelioid malignant mesothelioma gets caught, surgery. And chemotherapy is probably treatment options. However, the late diagnosis may limit patients to the palliative care because they are too weak to handle treatment side effects.
Because epithelioid mesothelioma cells respond best to treatment. A patient of this nature may be considered for a more aggressive treatment plan. Patients with epithelioid mesothelioma who have been diagnosed with cancer cells are often suitable for multimodal therapy. It tries to kill cancer cells with several types or therapeutic methods. The multimodal therapy combines the most of effective cancer therapies for mesothelioma, including surgery, chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
Dr. David Sugarbaker's impressive survival in 1999 led to a group of pleural mesothelioma. Patients with malignant epithelioid cells received multimodal therapy, including extrapleural pneumonectomy, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy. About 46 percent of patients had epithelioid cell types. No of lymph node involvement and no remaining cancer cells after surgery lived for at least five years. It typical 5-year survival of mesothelioma cancer is about 10 percent.
Less than half of the epithelial patients are suitable for aggressive surgery and multimodal therapy. And more than half are diagnosed too late, regardless of cell type, to qualify for surgery. If surgery is not possible, chemotherapy is considered standard therapy and clinical trials are discussed.
Common Mesothelioma Treatment Options
In malignant epithelioid mesothelioma, the most of the common treatment plan is a combination of surgery. Chemotherapy and radiation, commonly used together in a technique called multimodal treatment. Mesothelioma currently has no cure. The main goal is to eliminate or relieve symptoms and provide the patient with the longest possible life expectancy.
Surgery
For patients who are otherwise in good health, this potentially curative operation removes the entire lung, the mesothelium (lung lining). Half of the diaphragm and pericardium (heart food) on this page. This is the major operation with the high complication rate if the patient meets the requirements. Some researchers argue that it may possibly cure the disease.
- Curative or palliative used
- Targeted treatment
- Will remove as much as possible from cancer or reduce pain and discomfort. For example, by removing the fluid accumulations that can burden the affected organs
Chemotherapy
This therapy can reduce the size of mesotheliomas or decrease their progression. However, this positive answer is not permanent. These drugs attack which makes the cancer cells different than the healthy cells. This is based on the understanding the specifics of this cancer, as the genetic changes between the two patients with the same cancer may differ.
- Curative or palliative used
- Treats mesothelioma cells throughout the body
- It designed to the destroy cancer cells and shrink tumors to relieve associated symptoms
Radiation Therapy
In mesothelioma, radiotherapy is usually not very effective, as the tumor is rarely included in one area. This makes it difficult or impossible to focus the radiation waves only on the affected tissue.
- Targeted treatment
- Kill cancer cells
- It is known to help with pain and shortness of breath
If an epithelioid mesothelioma is the treated, you can undergo the same treatment as the other mesothelioma types. The good news is that the this treatment is much more effective than the treatment with other types of mesothelioma cancer.
There are a number of patients who can receive extrapleural pneumonectomy and whose life expectancy has been shown to increase. You may perform a pleurectomy with decortication (P / D) if the cancer has not entered the lungs.
If you have epithelioid peritoneal mesothelioma, you should consider cytoreductive surgery. There are no stages with peritoneal mesothelioma. Therefore, it is always the best to work with a specialist and get a second opinion.
Other the treatment options such as the chemotherapy and even radiation can be used. Alternative treatments such as gene therapy or even intensity modulated radiation have been shown to be effective.
There are a number of patients who can receive extrapleural pneumonectomy and whose life expectancy has been shown to increase. You may perform a pleurectomy with decortication (P / D) if the cancer has not entered the lungs.
If you have epithelioid peritoneal mesothelioma, you should consider cytoreductive surgery. There are no stages with peritoneal mesothelioma. Therefore, it is always the best to work with a specialist and get a second opinion.
Other the treatment options such as the chemotherapy and even radiation can be used. Alternative treatments such as gene therapy or even intensity modulated radiation have been shown to be effective.
Prognosis of Epithelioid Mesothelioma Is Good
The best prognosis is associated with mesotheliomas consisting of epithelioid cells. The median survival in epithelioid mesothelioma is about one year after diagnosis. By comparison, patients with sarcomatous mesothelioma live on average for six months. The improved the prognosis is about 200 days on average but can be years. If the cancer is diagnosed early.
In a meanwhile well-known Swedish study from 1996, the tumor cell type was examined in 85 cases of pleural mesothelioma as a prognosis factor. Patients with the epithelioid mesothelioma survived about 200 days longer than patients with sarcomatous or biphasic cell types. The with the tubulopapillary cells, a subtype of epithelioid mesothelioma. Lived 275 days longer than the patients with the other cell types. Overall, an epithelioid mesothelioma is associated with the better response to treatment and longer survival. This cell type can be open a window for the patients to access aggressive treatment plans and innovative clinical trials.
Cancer stages are based on the TNM classification, which assesses the patient's cancer based on three factors: tumor, lymph nodes, and distant metastases. The researchers and doctors want to know to what extent the tumor has formed. How far and how deep is it embedded in other tissues when it has traveled? The patient is informed that the cancer is in the "1 to 4" stage. These levels are the cumulative assessment of the TNM classification. In one study, the difference in prognosis and survival between patients with epithelioid mesothelioma was diminished. All of the these patients received surgery and a mix of chemo and radiotherapy.
In a meanwhile well-known Swedish study from 1996, the tumor cell type was examined in 85 cases of pleural mesothelioma as a prognosis factor. Patients with the epithelioid mesothelioma survived about 200 days longer than patients with sarcomatous or biphasic cell types. The with the tubulopapillary cells, a subtype of epithelioid mesothelioma. Lived 275 days longer than the patients with the other cell types. Overall, an epithelioid mesothelioma is associated with the better response to treatment and longer survival. This cell type can be open a window for the patients to access aggressive treatment plans and innovative clinical trials.
Cancer stages are based on the TNM classification, which assesses the patient's cancer based on three factors: tumor, lymph nodes, and distant metastases. The researchers and doctors want to know to what extent the tumor has formed. How far and how deep is it embedded in other tissues when it has traveled? The patient is informed that the cancer is in the "1 to 4" stage. These levels are the cumulative assessment of the TNM classification. In one study, the difference in prognosis and survival between patients with epithelioid mesothelioma was diminished. All of the these patients received surgery and a mix of chemo and radiotherapy.
- Patients with an epithelioid mesothelioma had a 2-year survival rate of 50 percent and a 3-year survival rate of 42 percent.
- Patients with the rarer sarcomatous mesothelioma had a 2-year survival rate of 7.5 percent and none of the patients had exceeded the last 25 months.
The median survival of a patient with epithelioid mesothelioma is 12 to 24 months. Compared with 12 months in biphasic patients and 6 months in sarcoma patients. As with the diagnosis and treatment plans, the prognosis varies from patient to patient and depends on several factors. In the overall forecast, those who are multimodal have a better prognosis. And the longer life expectancy compared to those that lead exclusively to palliative treatments. The combination therapy also had a positive effect on survival rates, with pemetrexed and cisplatin being promising when co-administered.
The cell type is a very an important factor that can be significantly affect a patient's mesothelioma prognosis. Those with epithelioid mesothelioma have a better prognosis than those with biphasic or sarcomatoid cell types.
There was a study that found that about the 60% of patients were diagnosed with an epithelioid mesothelioma. And treated for it, lived at least a year after the start of treatment. About 25% lived more than 5 years.
Epithelioid Mesothelioma Life Expectancy
Median survival in patients diagnosed with epithelioid mesothelioma is 18 to 24 months. Treatment options have a much more positive effect on life expectancy than sarcomatous mesothelioma. 60% of the epithelioid patents showed a survival rate of more than one year after the treatment. This is in part due to the fact that the type of epithelioid is much less aggressive than a sarcoma and responds more responsively to the treatment.
Nuclear grading is used by many to determine life expectancy. Epithelioid cells have a well-defined nucleus and are therefore an excellent competitor for the staff. The patients with a nuclear grade of 1, the median survival of the patient is 28 months. Increased scores lead to lower survival rates, with Grade 2 averaging 14 months and Grade 3 averaging 5 months.
Although the life expectancy is bleak for all of malignant mesothelioma types. The research and emerging treatments still create the hope to improve the lives of diagnosed patients. And the offer more options to extend the survival and contribute to healing.
Nuclear grading is used by many to determine life expectancy. Epithelioid cells have a well-defined nucleus and are therefore an excellent competitor for the staff. The patients with a nuclear grade of 1, the median survival of the patient is 28 months. Increased scores lead to lower survival rates, with Grade 2 averaging 14 months and Grade 3 averaging 5 months.
Although the life expectancy is bleak for all of malignant mesothelioma types. The research and emerging treatments still create the hope to improve the lives of diagnosed patients. And the offer more options to extend the survival and contribute to healing.
What Are the Characteristics of Epithelioid Cells?
Tumors are classified according to the type and appearance of the affected cells. The epithelioid epithelium is the most common epithelium in the four major tissue types in humans. These types include an epithelioid, connective, the muscular and nervous tissue. With the features like protection, the sensory perception, and fluid secretion. An epithelioid tissue encloses several large body cavities and most organs. The epithelioid cells are also present in the skin, eyes, taste buds and ears.
The structure of the epithelioid tissue varies according to location and function. Epithelioid cells can look thin and flat and have the shape of cubes, hexagons or columns. When the epithelial cells become cancerous, they can adopt various visual patterns: epithelioid, sarcoid and biphasic. Usually, they lose their unity or become atypical in other ways. You can also make small tubes or grapes that are reminiscent of a raspberry. The cancer cells are often differentiated according to their growth and spread as well as their shape and size. Although epithelial cells, with their uniform formation, do not spread as rapidly as sarcomatoid cells, they spread locally and into the lymph nodes.
In terms of location, epithelioid mesothelioma is most commonly based on pleura and is located in the lung lining. Can also be found in the abdomen, genitals and other reproductive areas. When looking at the cell shape, the focus is on epithelial cells with a well-defined nucleus that can be used as a determining factor in the cell type during the biopsy. Typically, epithelioid mesothelioma cells are flat or cube-shaped. However, when they become the cancerous, they can take different forms depending on the subtype.
The structure of the epithelioid tissue varies according to location and function. Epithelioid cells can look thin and flat and have the shape of cubes, hexagons or columns. When the epithelial cells become cancerous, they can adopt various visual patterns: epithelioid, sarcoid and biphasic. Usually, they lose their unity or become atypical in other ways. You can also make small tubes or grapes that are reminiscent of a raspberry. The cancer cells are often differentiated according to their growth and spread as well as their shape and size. Although epithelial cells, with their uniform formation, do not spread as rapidly as sarcomatoid cells, they spread locally and into the lymph nodes.
In terms of location, epithelioid mesothelioma is most commonly based on pleura and is located in the lung lining. Can also be found in the abdomen, genitals and other reproductive areas. When looking at the cell shape, the focus is on epithelial cells with a well-defined nucleus that can be used as a determining factor in the cell type during the biopsy. Typically, epithelioid mesothelioma cells are flat or cube-shaped. However, when they become the cancerous, they can take different forms depending on the subtype.
Cell Prevalence
An epithelioid mesothelioma is the most common cell type and also has the best prognosis. You will find that it is the most common in men who are white and over 45 years old. They are the square and have visible nuclei (plural for "nucleus", the center of the cell that carries genetic material). Specialists are more likely to differ from other mesothelioma cell types because of their unique appearance.
Cell Description
These cell types have defined the elongated egg shape. The visible nuclei make to this cell the easiest to distinguish. Tumors from epithelial cells grow quickly. These cells replicate the faster than sarcomatous or biphasic mesothelioma tumors. However, due to the quadratic shape of the epithelioid cells, they stick together and slow their propagation into other parts of the body.
Cell Behavior
A tumor with these cells will grow much faster because they divide very quickly. They cling to the each other, which means that it does not spread so quickly. Epithelioid mesothelioma is most responsive to treatment as it is slower to metastasize than other cell types.
Because epithelial cells lack mobility and adhere tightly, they spread less frequently than sarcoid cells in remote locations. An epithelioid cell mainly spread to nearby the lymph nodes and migrate locally through the lymphatic system. Conversely, the sarcomatoid cells are loosely organized and can easily migrate, resulting in faster metastasis.
Epithelioid cells are more common in malignant pleural mesothelioma than peritoneal mesothelioma. A specific type of epithelioid mesothelioma is more common in women and is referred to as differentiated papillary mesothelioma. No other the cell type is associated with the particular gender, age or race.
Because epithelial cells lack mobility and adhere tightly, they spread less frequently than sarcoid cells in remote locations. An epithelioid cell mainly spread to nearby the lymph nodes and migrate locally through the lymphatic system. Conversely, the sarcomatoid cells are loosely organized and can easily migrate, resulting in faster metastasis.
Epithelioid cells are more common in malignant pleural mesothelioma than peritoneal mesothelioma. A specific type of epithelioid mesothelioma is more common in women and is referred to as differentiated papillary mesothelioma. No other the cell type is associated with the particular gender, age or race.
Epithelial Mesothelioma Subtypes
Under the epithelioid mesothelioma, there are the several subtypes that vary according to cellular structure, location, and symptoms. The subtype can affect the side effects, treatment, and prognosis of the mesothelioma patient. There are a number of epithelioid mesothelioma subtypes. They have differences in size, shape and uniform structure. Each of the subtypes can react differently to different treatment types.
Epithelial cells come in different shapes and sizes. Each cellular subtype responds differently to the treatment. Some of the subtypes are more common than the others, making them easier to diagnose and treat.
An epithelioid mesothelioma has many subtypes, each with its own unique characteristics. Some subtypes tend to develop in certain areas of the body, while others are extremely rare. While the subtype you do not control does not affect your treatment, it helps physicians distinguish mesothelioma from similar cancers. Below are technical descriptions of some cell patterns doctors have seen in epithelioid mesothelioma.
Epithelial cells come in different shapes and sizes. Each cellular subtype responds differently to the treatment. Some of the subtypes are more common than the others, making them easier to diagnose and treat.
An epithelioid mesothelioma has many subtypes, each with its own unique characteristics. Some subtypes tend to develop in certain areas of the body, while others are extremely rare. While the subtype you do not control does not affect your treatment, it helps physicians distinguish mesothelioma from similar cancers. Below are technical descriptions of some cell patterns doctors have seen in epithelioid mesothelioma.
Tubulopapillary
In tubulopapillary the cell pattern is one of the most common subtypes of epithelioid mesothelioma. Most tubulopapillary mesothelioma contains well-differentiated cells. The doctors may mistake this subtype for an adenocarcinoma that has spread to the pleura.
Adenomatoid
These cells, called glandular or microglandular mesothelioma, may be flat or cuboidal and surround the glands. This can make it difficult to the distinguish it from adenocarcinoma. Adenoid epithelial cells are present in all types of mesothelioma. Because it looks like the other tumors, it can be difficult to accurately diagnose a patient.
Adenomatoid mesothelioma, also known as microglandular subtype. Affects 6 percent of all cases of pleural mesothelioma. These tumors consist of smooth cells that are flat to cubic in shape and are lined by small glandular structures.
They often occur the alongside other subtypes, but may also be the dominant cell pattern. For physicians, it can be difficult to distinguish this subtype from other tumors.
Adenomatoid mesothelioma, also known as microglandular subtype. Affects 6 percent of all cases of pleural mesothelioma. These tumors consist of smooth cells that are flat to cubic in shape and are lined by small glandular structures.
They often occur the alongside other subtypes, but may also be the dominant cell pattern. For physicians, it can be difficult to distinguish this subtype from other tumors.
Solid
The fixed subtype has two patterns: good and poorly differentiated.
The well-differentiated is one of the most common cell patterns in mesothelioma cancer. Their round cells form nests, cords or cloths. The poorly differentiated the pattern has relatively disorganized the cells whose appearance is polygonal.
A well-differentiated the mesothelioma can be confused with benign reactive mesothelioma hyperplasia. The poorly differentiated the pattern seems to be similar to lymphoma and large cell carcinoma.
The well-differentiated is one of the most common cell patterns in mesothelioma cancer. Their round cells form nests, cords or cloths. The poorly differentiated the pattern has relatively disorganized the cells whose appearance is polygonal.
A well-differentiated the mesothelioma can be confused with benign reactive mesothelioma hyperplasia. The poorly differentiated the pattern seems to be similar to lymphoma and large cell carcinoma.
Small Cell Mesothelioma
Small cell mesothelioma has its own shape. You will find that this is most common when looking at a peritoneal mesothelioma. It will be the hardest to deal with.
This is a very rare form of epithelioid mesothelioma, first discovered in 1992. She sees other small-celled cancers, such as Pathologists diagnose small cell mesothelioma by cytological analysis (viewing cells by enlargement).
This is a very rare form of epithelioid mesothelioma, first discovered in 1992. She sees other small-celled cancers, such as Pathologists diagnose small cell mesothelioma by cytological analysis (viewing cells by enlargement).
Glandular
The tumors with the glandular pattern usually consist of axillary or glandular structures. This subtype usually develops in the pleural lining. It can be mistaken for an adenocarcinoma that has spread to the pleura.
Cystic Mesothelioma
Cystic mesothelioma will be the rarest. It is found in peritoneal mesothelioma. There are more women affected than men.
This is incredibly rare and usually benign. It is found in women of childbearing age and traditionally in the abdomen. The disease forms a mesothelioma-lined cyst surrounded by fibrous tissue. Surgery is the most common treatment.
This is incredibly rare and usually benign. It is found in women of childbearing age and traditionally in the abdomen. The disease forms a mesothelioma-lined cyst surrounded by fibrous tissue. Surgery is the most common treatment.
Deciduoid Mesothelioma
This rare subtype can occur in the abdomen of women who have not been exposed to asbestos, or in the lungs of men and women. This cancer is treated to like a normal epithelioid mesothelioma. However, it can be very aggressive, depending on the shape of the cells.
Deciduoid mesothelioma is a rare cell when it is found in pleural mesothelioma. It is actually the more common when it is found in the peritoneal cavity, and it is found in about 50% of cases. Deciduoid mesothelioma is a rare epithelial subtype that can be caused by factors other than exposure to asbestos. This pattern has to the large round to polygonal cells with sharp edges.
Since it is so unusual, a definite mesothelioma can be confused with other diseases. These include squamous cell carcinoma, anaplastic large cell lymphoma and the gastrointestinal autonomic tumor. Pseudotumoral deciduous, trophoblastic tumors and the oxyphilic variant of ovarian cell carcinoma.
Papillary Mesothelioma
The papillary mesothelioma is not very aggressive, but it is rare and can not be seen as often. It can be seen in the peritoneum. A slow-growing variant that does not spread is a differentiated papillary mesothelioma in which papillae are lined with a single layer of flat mesothelioma cells. This species usually affects young women and is not associated with asbestos exposure.
This is very rare epithelioid mesothelioma occurs predominantly in the abdomen of women. It is the technically cancerous, but it is not to aggressive and rarely metastasizes. After surgery, most patients will not experience recurrences.
Small cell mesothelioma can be considered as an additional subtype of mesothelioma but is typically diagnosed in biphasic tumors that have a combination of epithelial and sarcomatoid cells. In some cases, multiple biopsies may be needed to confirm a diagnosis. The doctors need to carefully analyze the cancer cells to understand a patient's cancer. These forms are not only the confused with the other subtypes under the mesothelioma roof, they are also often misdiagnosed as other diseases. The misdiagnosis can significantly affect effective treatment and life expectancy.
This is very rare epithelioid mesothelioma occurs predominantly in the abdomen of women. It is the technically cancerous, but it is not to aggressive and rarely metastasizes. After surgery, most patients will not experience recurrences.
Small cell mesothelioma can be considered as an additional subtype of mesothelioma but is typically diagnosed in biphasic tumors that have a combination of epithelial and sarcomatoid cells. In some cases, multiple biopsies may be needed to confirm a diagnosis. The doctors need to carefully analyze the cancer cells to understand a patient's cancer. These forms are not only the confused with the other subtypes under the mesothelioma roof, they are also often misdiagnosed as other diseases. The misdiagnosis can significantly affect effective treatment and life expectancy.
Focus On What You Can Control
There are things that you can control when it comes to your prognosis. You can not control the cell type of your cancer or how it will ultimately affect your lifespan. However, there are other prognostic factors that you can control, such as: the treatments selected and the choices you make.
The participating in the clinical trials, improving your diet and exercising regularly will strengthen your immune system. You can work with a specialist in palliative care to treat symptoms and improve quality of life.
These are some of the steps that you can take to extend your life with epithelioid mesothelioma cancer. In addition to the right treatment and the help of a mesothelioma specialist, the average prognosis of mesothelioma can be survived.
The participating in the clinical trials, improving your diet and exercising regularly will strengthen your immune system. You can work with a specialist in palliative care to treat symptoms and improve quality of life.
These are some of the steps that you can take to extend your life with epithelioid mesothelioma cancer. In addition to the right treatment and the help of a mesothelioma specialist, the average prognosis of mesothelioma can be survived.








COMMENTS